Condensate pumps represent a special group of power pumps characterized by specific operating conditions: operation under conditions of deep vacuum and minimal geometric support. This reserve is due to the difference in vertical marks of the liquid’s free surface level in the condenser and the center of gravity of the inlet opening of the first-stage impeller of the pump (geometric support) and losses in the pump’s inlet tract.
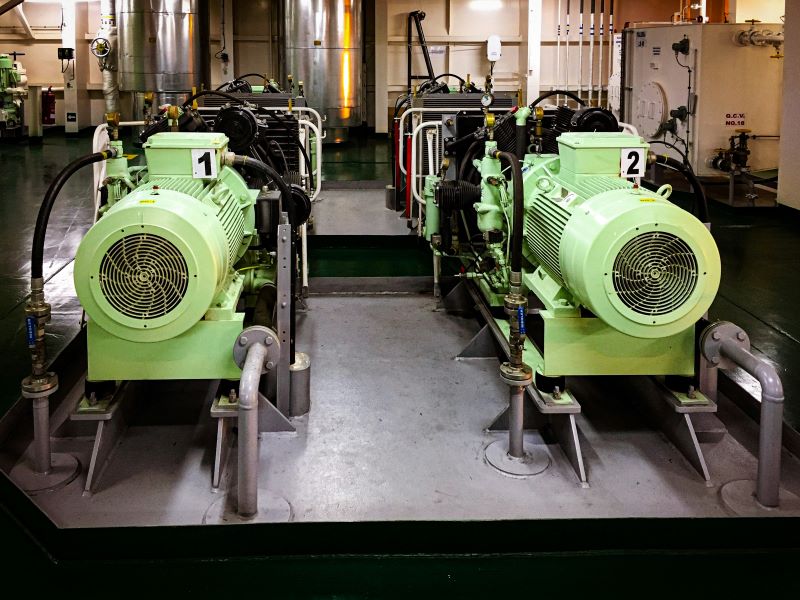
Condensate pumps are crucial units of auxiliary equipment in thermal power plants.
Condensate pumps are designed to transfer condensate in steam-water networks of thermal power plants operating on organic fuel, as well as liquids similar to condensate in viscosity and chemical activity.
The main parameters of condensate pumps are regulated by GOST 6000-88. Depending on the parameters, they have a uniform and highly standardized design.
All produced condensate pumps can be grouped into several structurally similar groups. Within each group, pumps have many common design features and solutions with minor differences in the construction of individual components.
Small and medium-sized condensate pumps of thermal power plants are horizontal multistage sectional pumps of the Ks or spiral KsD type. With increasing parameters of condensate pumps, mainly capacity, their dimensions and weight increase. Therefore, in practice, condensate pumps of thermal power plants with a capacity of 200 m³/h and above are manufactured in a vertical design of the KsV type.
Condensate pumps are divided into first and second lift pumps for main condensate and drainage. First lift pumps transfer condensate from the turbine condenser through a block cleaning unit to the inlet of second lift pumps, which supply condensate through low-pressure heaters to the deaerator.
Condensate pumps must operate reliably in the presence of initial or developed stages of cavitation in the area of the impeller, and in some cases, even with supercavitational flow around the impeller elements.
To improve cavitation characteristics and reduce cavitation erosion, a screw-centrifugal stage is used.
The specific operating conditions of condensate pumps have defined the main requirements for their design:
- ensuring reliable and long-term operation (at least 15000 hours) with partial cavitation in the pump;
- absence of air suction through both working and non-working pumps;
stable continuously dropping shape of the head characteristic in the range of flow rates from 20% to 110% of the rated to ensure stable parallel operation in the overall network.
To expand the range of application of condensate pumps, it is permissible to trim the impellers by no more than 10% of their initial diameter. At the same time, the decrease in efficiency should not exceed 3%.
- To reduce the harmful effects of cavitation and ensure reliable operation of condensate pumps, the following duration of operation is recommended in flow rate ranges:
- from 0 to 0.2 – no more than 3 minutes;
- from 0.2 to 0.5 – up to 5% of the total pump running time;
- from 0.5 to 0.85 – no more than 15% of the total pump running time;
- from 0.85 to 1.05 – without limitation;
above 1.05 – according to the conditions of the motor load and cavitation reserve at the inlet.
- The materials of the main components of condensate pumps are gray cast iron, carbon and alloy steels. Chromium steels are used for the first-stage impellers and pre-swirl axial wheels.