The Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries, a group of Arab states in the Persian Gulf region, have
held a unique position in the global division of labor for many decades. Leveraging their natural
advantage in energy resources, these Gulf nations have been pivotal players in the global energy
market.
Despite the continued significance of oil and gas revenues in the economies of GCC countries in the near
future, these nations have clearly set a course for diversification and the development of a digital
economy and other technological sectors. In this region, there are all the prerequisites for achieving
leadership in the fields of information technology (IT) and digitization, including substantial investment
resources, robust infrastructure, and thriving startup ecosystems.
In terms of internet penetration, five out of the six GCC countries (with Oman being the exception) rank
among the top five in the world. In Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Bahrain, the UAE, and Kuwait, internet usage is
at 100% among the population. This strong digital foundation provides a solid basis for their digital
transformation and innovation efforts.

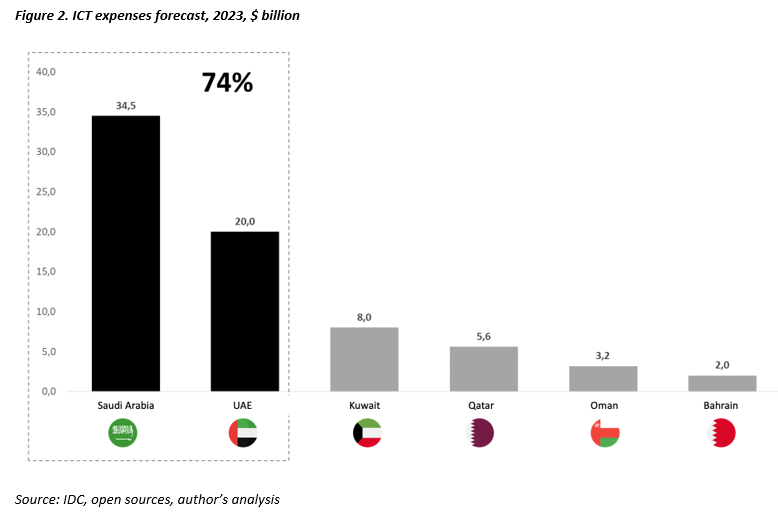
The total ICT (Information and Communication Technology) spending in GCC countries is projected
to reach $73.3 billion in 2023, which is nearly comparable to the ICT market in Russia
(approximately 80 billion USD when converted at the average exchange rate of the ruble in 2022).
However, it’s important to note that the combined population of the six GCC countries is about 2.5
times smaller than that of Russia, with 59.4 million in GCC compared to 146.4 million in Russia. The
main drivers of ICT market growth in the GCC are Saudi Arabia and the UAE, accounting for 74% of
all expenditures among GCC countries.
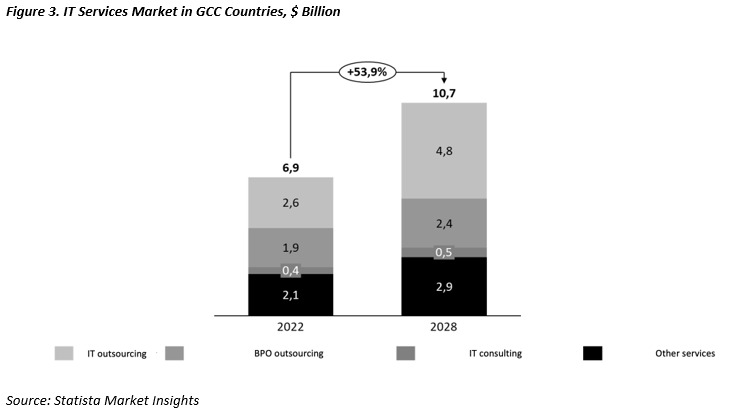
Approximately 10% of the entire ICT (Information and Communication Technology) market is composed
of IT services, with the largest portion being IT outsourcing. The IT services market is in an advanced
stage of maturity, and according to Statista, the projected growth rate is expected to be around 8% per
year over the next 5-6 years.
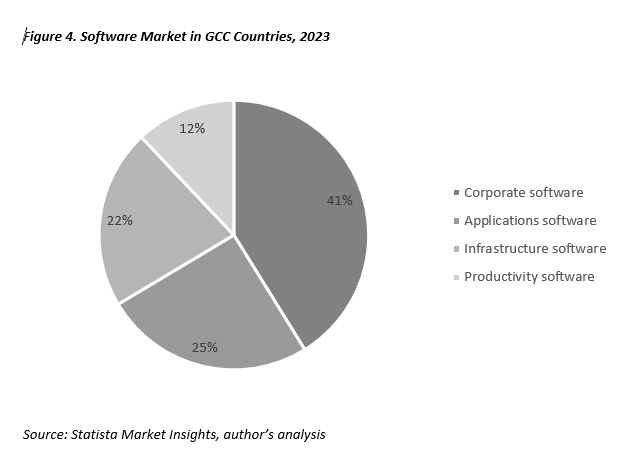
The software market in GCC countries is projected to reach $4 billion in 2023. Corporate software,
including ERP systems, CRM, BI, and more, dominates the market structure, accounting for over 40%.
The market is expected to grow at a rate of 3% to 5% over the next five years.
The development of the IT sector and digitization in recent years have been a focal point of the government policies in GCC countries. Each country is implementing projects and programs to promote IT development in line with their long-term strategies:
- In the UAE, there are state-level strategies for the development of AI and blockchain technologies. They are implementing a project to create a hub for technological innovation and attract IT companies in Dubai, known as Dubai Internet City.
- Qatar is creating an innovation cluster for digital technologies known as TASMU Digital Valley.
- Bahrain has adopted a Digital Government Strategy for 2022, outlining their strategy for developing a digital state.
These digital projects are also embedded in higher-level documents:
- Kuwait plans to develop IoT and fiber optic communication as part of their national development plan.
- Saudi Arabia is focusing on the development of e-commerce and fintech.
- Oman is working on IT infrastructure development and eGovernment initiatives to become a digital state.
Saudi Arabia is undertaking mega-projects like “Neom” (a futuristic city) and “AMAALA” (building luxury resorts and developing ecotourism on the Red Sea coast). These projects require significant investments in digital infrastructure, modern technologies like AI/ML, IoT, edge computing, and 5G.
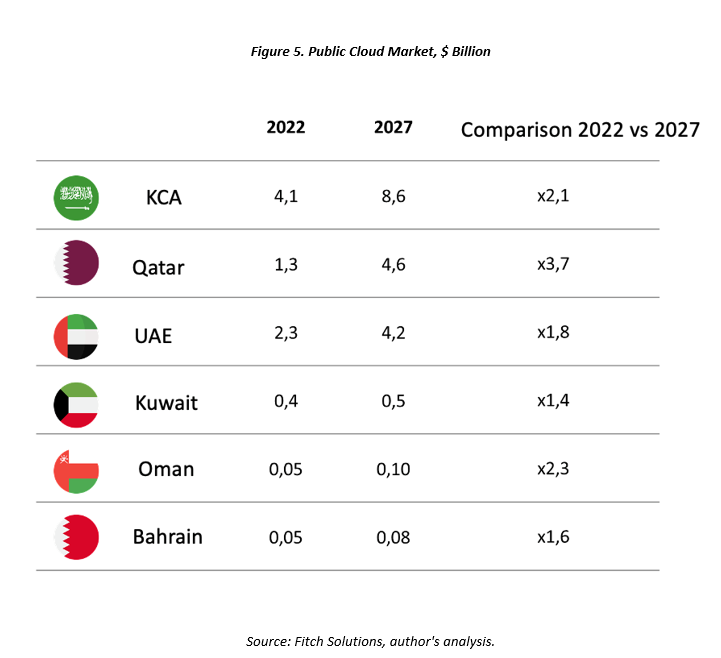
The digitization of GCC countries’ economies requires advanced infrastructure, including data storage. Local companies have historically relied on foreign infrastructure. Amazon Web Services (AWS) opened its first data center in Bahrain in 2019, and the second one in the UAE in 2022. Saudi Aramco, Saudi Arabia’s largest oil company, partnered with Google Cloud in 2022 to develop cloud services in the country. In the same year, two joint data centers were established by STC (the largest telecommunications company in Saudi Arabia) and Alibaba (China). The cloud services market in GCC countries is expected to exceed $18 billion by 2027, indicating a more than twofold growth over the next five years.
Industrial and service sector diversification in GCC countries is being carried out using modern technologies and equipment, enabling real-time data collection and analysis. Saudi Arabia is undertaking mega-projects such as “Neom” (a futuristic city) and “AMAALA” (building luxury resorts and developing ecotourism on the Red Sea coast), which require significant investments in digital infrastructure and platforms, modern AI/ML (Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning) technologies, IoT (Internet of Things), edge computing, 5G, and more.
The technology of “digital twins” was vividly demonstrated at the FIFA World Cup in Qatar when approximately 40,000 IoT devices were used to manage massive crowds of fans. In Dubai, the EC3 control center uses AI technology, digital cameras, and thermal imaging technology to manage 11,000 surveillance cameras, 5,000 km of roads, 10,000 taxis, and more. Continued investments in tourism development and hosting international events, such as the Winter Asian Games in the “smart” city of Neom in Saudi Arabia in 2029, are among the drivers of the IoT market’s growth. By 2030, according to Oliver Wyman’s forecast, there will be over 1 billion IoT connections in GCC countries.
The digitization of government services is actively progressing. Bahrain’s National Digital Transformation Strategy, adopted in 2022, involves consolidating existing government data for forecasting and decision-making purposes. In Saudi Arabia, over 130 government authorities are implementing data management functionalities, and Dubai’s government super app, Dubai Now, has processed 20 million transactions worth $2.7 billion since its launch in 2015. Similar apps to Dubai Now exist in Saudi Arabia (Tawakkalna Services), Kuwait (Sahel), and Qatar (Hukoomi).
Significant attention is being given to the development of AI. The governments of the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Qatar are investing more in AI than some European countries. For instance, Saudi Arabia has invested over $135 billion in the Softbank Vision Fund and aims to be among the top 15 countries in AI development by 2030. The UAE became the first country in the world to establish a Ministry of Artificial Intelligence. Oman, as part of “Vision 2040,” is also placing a strong emphasis on AI to enhance productivity and create new jobs.
The presence of long-term vision and substantial financial resources in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries will position the region as one of the key IT hubs in the world. It is anticipated that more than 45 unicorn startups (with valuations exceeding $1 billion) will emerge in the Middle East and North Africa region, with a significant portion of them originating from Saudi Arabia.
The main challenges for the development of the IT sector in the GCC region are related to attracting qualified workforce (many countries rely on expatriates to drive economic growth), providing infrastructure and comfortable living conditions for specialists, and maintaining political stability.